PR – Intra-op Virtual Measurements in Laparoscopic and Robotic-Assisted Surgeries
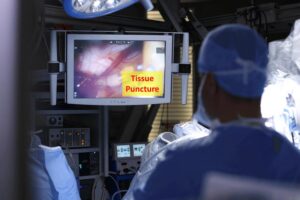
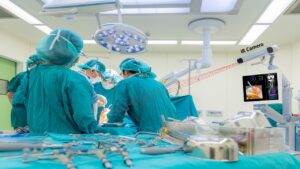
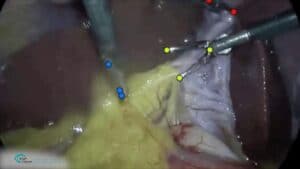
RSIP Vision Presents New Technology for Intra-op Virtual Measurements in Laparoscopic and Robotic-Assisted Surgeries Innovative Technology Provides Calibration of Robotic-Assisted Surgeries’ (RAS) Images and a Platform for Accurate Measurement, Especially During Trauma and Acute Care Surgery Cases. TEL AVIV, Israel & SAN JOSE, Calif., January 25, 2022 – RSIP Vision, an experienced leader in driving innovation for medical imaging through advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) and computer vision solutions, today announces a new supporting technology for intraoperative video analysis. This technology provides real-time, accurate anatomical measurements in surgical videos, supporting a

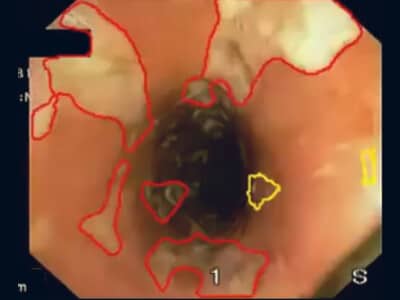
 Identify workflow stages
Identify workflow stages
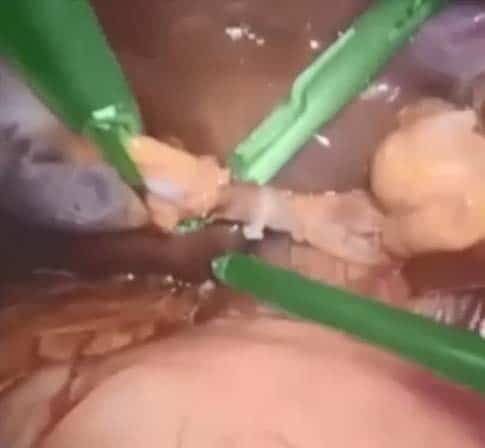
 Leveraging deep learning and classical image processing techniques
Leveraging deep learning and classical image processing techniques
 Applications
Applications
 Functionalities:
Functionalities: