PR – Intra-op Virtual Measurements in Laparoscopic and Robotic-Assisted Surgeries
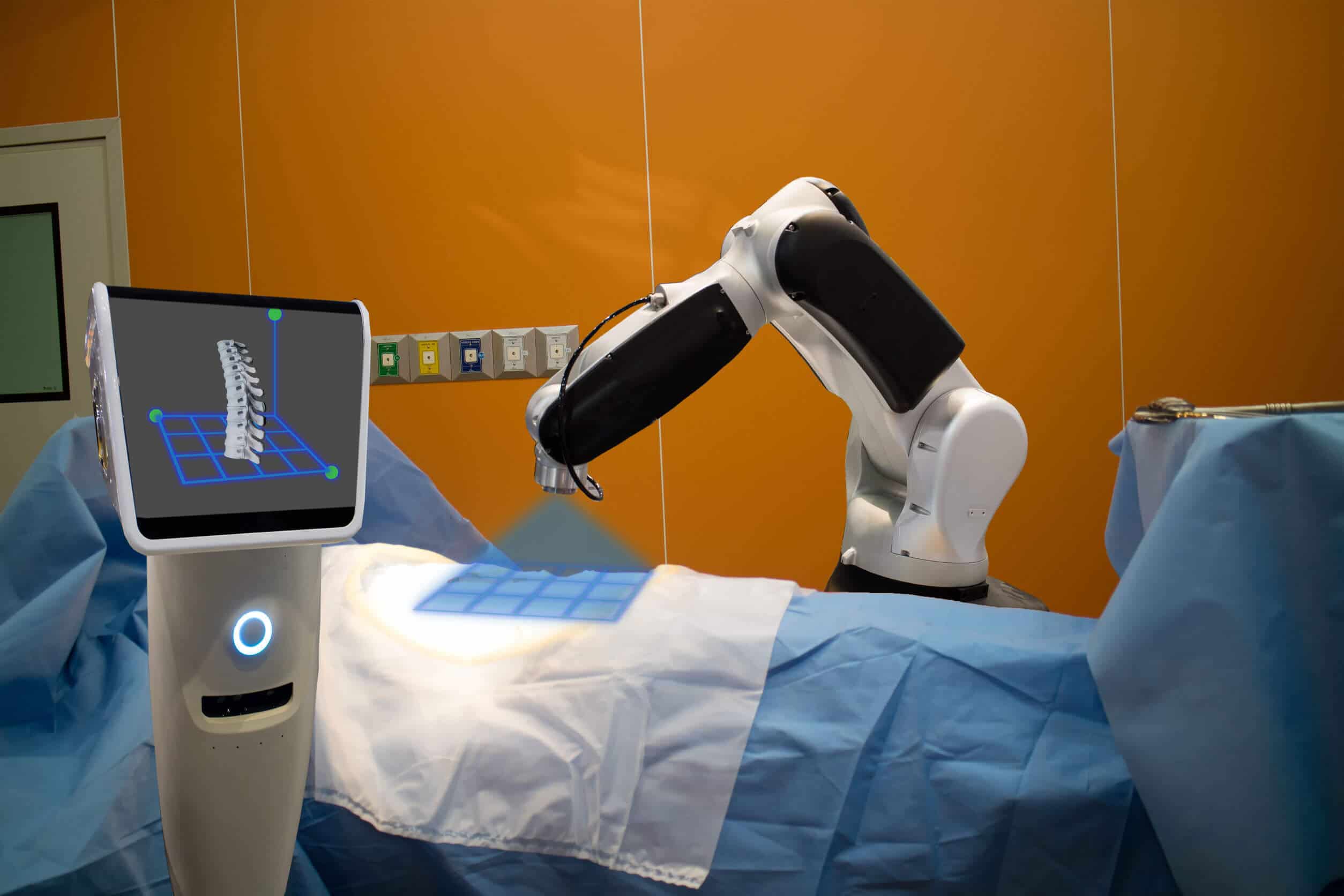
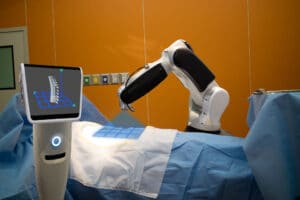
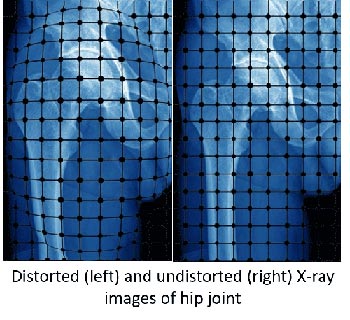
RSIP Vision Presents New Technology for Intra-op Virtual Measurements in Laparoscopic and Robotic-Assisted Surgeries Innovative Technology Provides Calibration of Robotic-Assisted Surgeries’ (RAS) Images and a Platform for Accurate Measurement, Especially During Trauma and Acute Care Surgery Cases. TEL AVIV, Israel & SAN JOSE, Calif., January 25, 2022 – RSIP Vision, an experienced leader in driving innovation for medical imaging through advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) and computer vision solutions, today announces a new supporting technology for intraoperative video analysis. This technology provides real-time, accurate anatomical measurements in surgical videos, supporting a

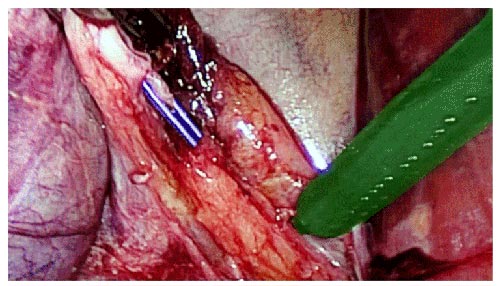
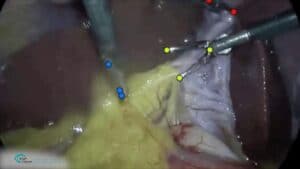
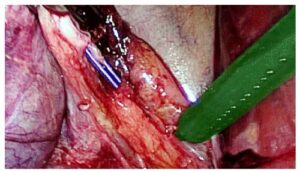 Tissue tracking throughout the procedure
Tissue tracking throughout the procedure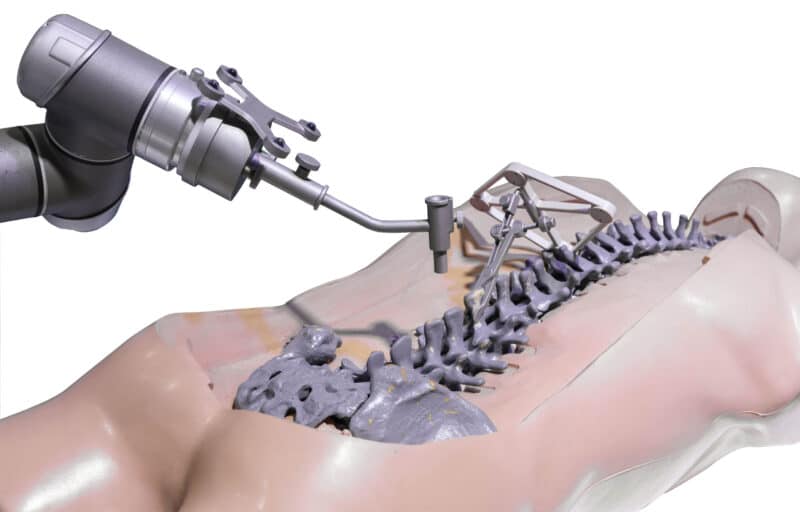
 Use RGB or IR cameras to track objects in the OR
Use RGB or IR cameras to track objects in the OR